Understanding Your Diabetes Risk: Prevention, Management, and Treatment Options
November 2024
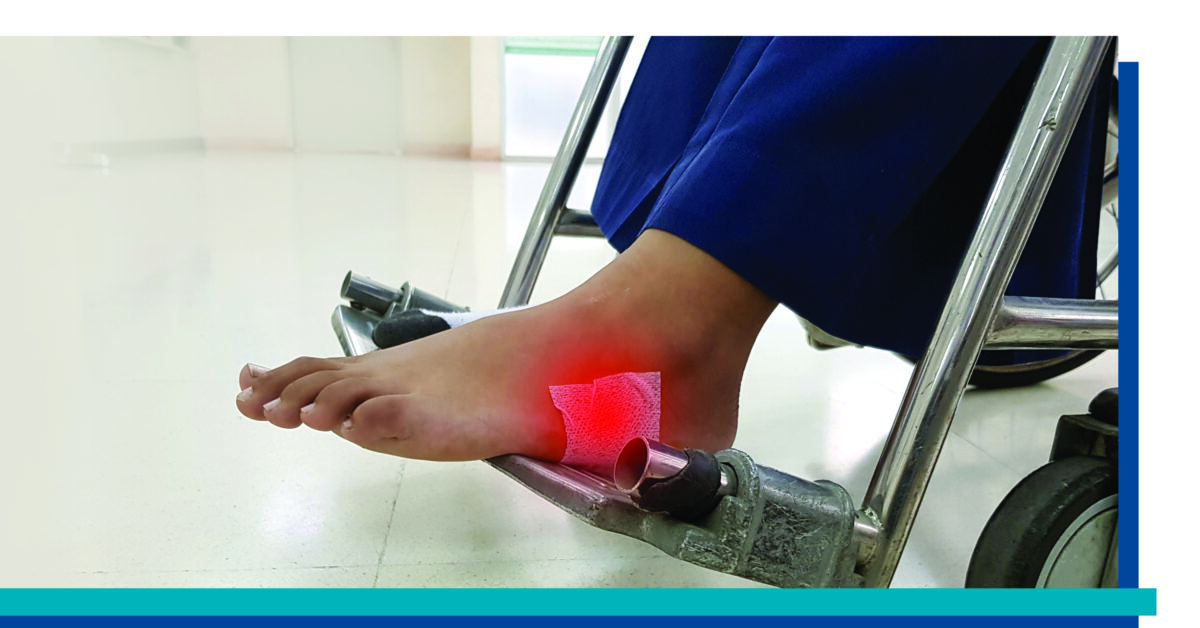
Take Steps to Prevent Foot Problems from Diabetes
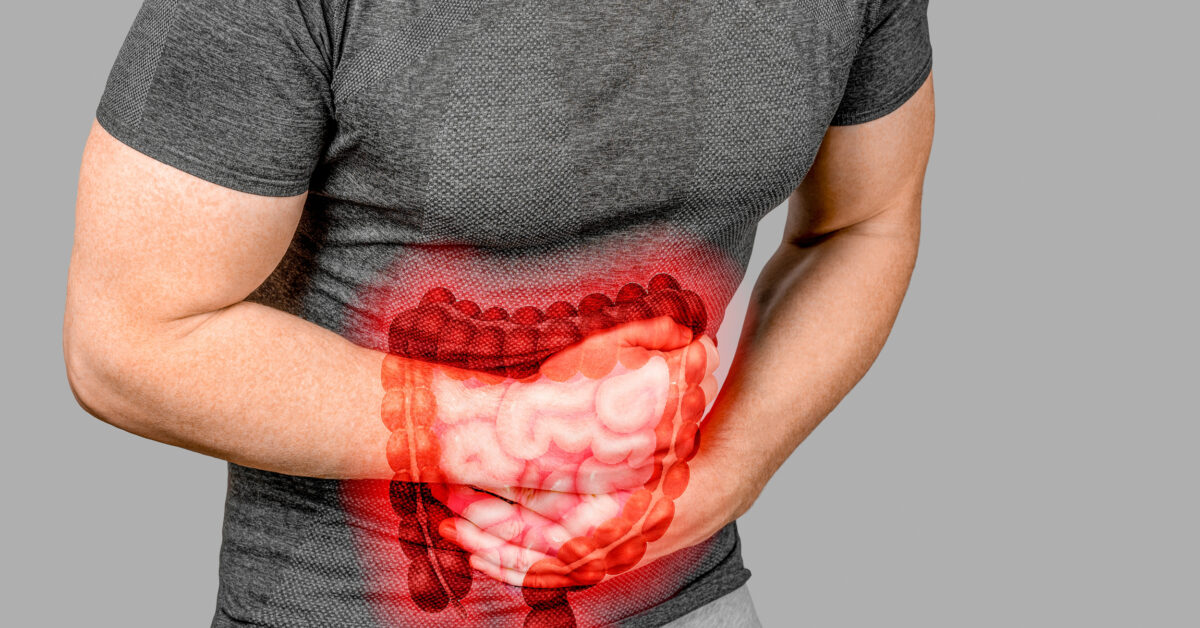
November 2024The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that there are 30.3 million people living with diabetes in the United States. Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing wounds, particularly on their feet, which can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly and properly.
Diabetics are prone to hard-to-heal wounds due to a combination of factors that make them more susceptible to developing wounds. The most significant of these factors include:
Peripheral neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, especially in extremities. This condition, known as “peripheral neuropathy,” can cause a loss of sensation in the feet. As a result, small cuts, blisters, or other injuries may go unnoticed, leading to infection or delayed healing.
Poor circulation: Diabetes also affects blood flow. High glucose levels can lead to the hardening and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis), which limit circulation to the body. This slows down the body’s ability to deliver oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to the wounds. As a result, the injuries heal slowly or may not heal at all.
Immune system dysfunction: Chronic high blood sugar levels impair the function of white blood cells. These cells are central to the role of the immune system. This makes it difficult to fight off infections and can lead to the rapid spread of bacteria if a wound is left untreated.
Diabetic wounds, particularly foot ulcers, are more than just a pain. They can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. If left untreated, diabetic wounds can result in severe infection. Because diabetics often have weakened immune systems, their wounds are more susceptible to infections. Once an infection sets in, it can spread rapidly to surrounding tissues, bones, and even the bloodstream (sepsis), posing a serious threat to overall health. Poor circulation, combined with infection, can even result in tissue death (gangrene). This condition may necessitate amputation to prevent the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Treating Diabetic Wounds
For hard-to-heal wounds, diabetic patients often enlist the help of a wound care specialist for treatment. This could include collecting tissue cultures to diagnose the cause of the infection and prescribe the most effective medications and/or other treatment options.
In some cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may also be an option. HBOT is a medical treatment that uses pure oxygen at two-to-three-times atmospheric pressure to aid in healing wounds. For patients who qualify, HBOT can help fight infection and speed healing.
During and after treatment, patients may be referred to services such as diabetes care or nutrition counseling that can help address the underlying causes of non-healing wounds. If appropriate, education for family members and caregivers may take place, teaching them how to perform wound care and how to use any prescribed products.
Lake Charles Memorial Health System is home to two convenient wound care clinics: Oak Park Blvd. and the newest edition at Imperial Pointe on Nelson Rd. Both locations are staffed with a team of doctors, nurses and therapists uniquely experienced in the healing of chronic wounds.