Take Steps to Prevent Foot Problems from Diabetes
November 2024
Industry Stewards
November 2024by Kerry Andersen
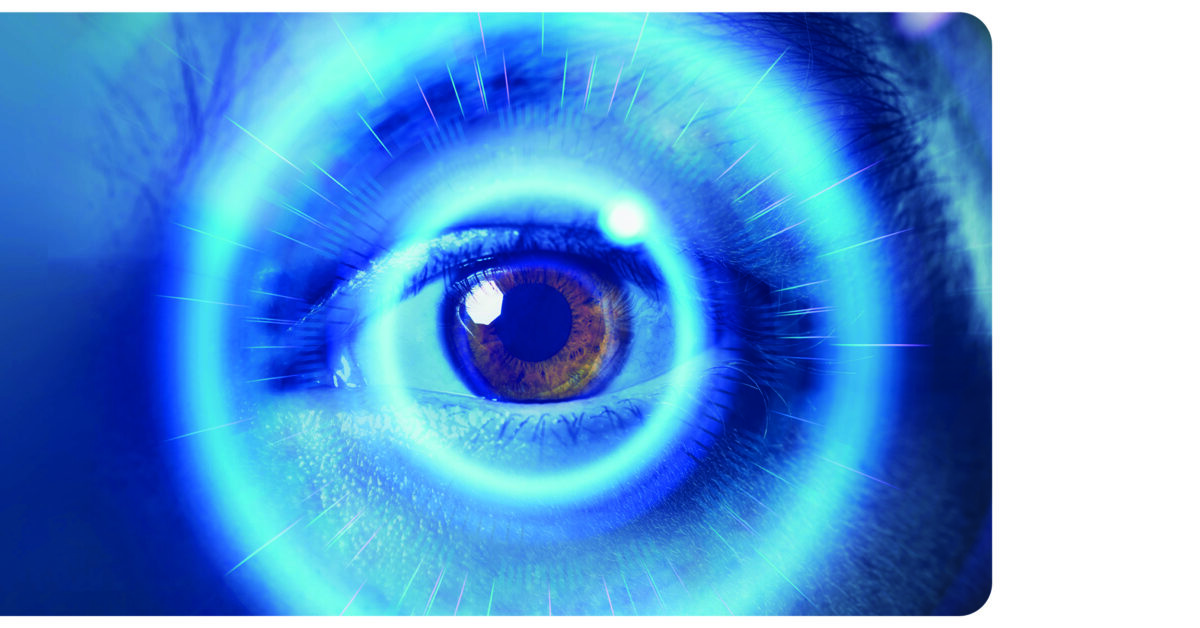
One of the most significant complications associated with diabetes is its impact on eye health. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a variety of vision problems. Dr. William B. Hart, MD, with Hart Eye Center in Lake Charles says diabetic eye disease encompasses several conditions, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. These conditions can lead to vision impairment or even blindness if not effectively managed.
Diabetic Retinopathy – The most common eye disease associated with diabetes occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina—the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. In early stages, blood vessels may swell and leak fluid, but in advanced stages, abnormal blood vessels grow on the retina’s surface, potentially causing severe vision loss or blindness. People with diabetes for a longer duration, especially those with poor blood sugar control, are at greater risk for developing this condition.
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) – This complication occurs when fluid accumulates in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. The swelling of the macula can lead to blurred vision, difficulty seeing fine details, and eventually, vision loss if left untreated. DME is the leading cause of vision loss among people with diabetic retinopathy.
Cataracts and Glaucoma – Cataracts occur when the eye’s lens becomes cloudy, making it difficult to see clearly. Diabetics tend to develop cataracts at a younger age, and the condition progresses faster than in those without diabetes. Glaucoma, on the other hand, is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure in the eye. Diabetic individuals are more prone to developing open-angle glaucoma, which can cause gradual vision loss if untreated.
Treatments for Diabetic Eye Conditions
Laser Therapy – Laser treatment is a common option for patients with diabetic retinopathy. During the procedure, lasers are used to seal off leaking blood vessels in the retina or to shrink abnormal vessels, helping to prevent further damage and preserve vision.
Injections – For individuals with diabetic macular edema, anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections can reduce swelling and improve vision. These medications work by blocking the protein that promotes abnormal blood vessel growth. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may also be used to reduce inflammation.
Surgery – In advanced cases of diabetic eye disease, surgical interventions may be necessary. For instance, vitrectomy surgery can help remove scar tissue and blood from the center of the eye, improving vision and reducing further complications. If cataracts become severe, cataract surgery is necessary to remove the clouded lens and replace it with an artificial one, restoring clarity to vision.
Dr. Hart stresses the earlier diabetic eye problems are diagnosed, the greater the likelihood for treatment or even elimination. “All of the diabetic eye complications can be delayed or avoided with good blood sugar control and especially annual eye exams. Prevention is the best therapy and that means routine eye exams.”
Strategies to Protect Your Eyes
Maintain Blood Sugar Levels – One of the most crucial steps in preventing diabetic eye complications is keeping blood sugar levels within the target range. Consistently high blood sugar damages blood vessels throughout the body, including in the eyes.
Regular Eye Exams – Annual comprehensive eye exams are essential for detecting early signs of diabetic eye disease. People with diabetes should schedule dilated eye exams, where an eye care specialist checks for retinal damage, even if there are no symptoms of vision loss.
Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol – High blood pressure and cholesterol can exacerbate the effects of diabetes on eye health. Managing these risk factors through medication, diet, and exercise can reduce the likelihood of developing complications like diabetic retinopathy.
Stop Smoking – Smoking increases the risk of diabetes-related complications, including those that affect the eyes. Quitting smoking can help improve overall eye health and reduce the risk of vision loss.
Even though diabetes can have a profound impact on eye health, with proper management, regular monitoring, and timely treatment, individuals can reduce the risk of developing vision-threatening complications. By controlling blood sugar levels, scheduling regular eye exams, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, those living with diabetes can protect their vision and maintain a better quality of life.
Hart Eye Center is located at 1920 W. Sale Road in Lake Charles. Learn more about diabetes eye health by visiting harteyecenter.com or calling 337.439.4014 to schedule an appointment.






